DL for Depth and Camera Pose
- Deep NNs can be trained to learn a mapping from input space
(can be images) to the label space (can be depth maps or camera poses). - Parameters are optimized using gradient descent over a loss function which measures the difference between the predicted and true labels.
- With the rise in scanners, we can easily generate data and also create our own synthetic datasets.
Depth Prediction
- In 2014 we first saw the use of deep learning for depth prediction. Link.
- This very simple idea of using a CNN to predict depth from a single image has been shown to work decently well, < this was also in Inverse Graphics as we saw >/
- Later on as time marches, ideas rise, we saw better architectures and better models.
Learning Feature Detectors and Descriptors
Indirect SLAM approaches rely on feature detectors and descriptors to extract a sparse set of visual measurements from the input images. First, salient regions of the images are identified, commonly refered to as keypoints. Then the local neigh- borhood of each keypoint is used to compute a vector descriptor which can be used to match keypoints between images.
Neural networks can be trained to replace the hand designed feature detectors and descriptors commonly used in SLAM and SfM pipelines. On such method, SuperPoint proposed using a convolutional neural network to both (1) detect salient image regions and (2) assign feature descriptors to the detected keypoints. Similiarly, Universal Correspondence Network , showed that feature descriptors produced by a neural network can improve downstream feature matching accracy. Such networks are typically trained using a contrastive loss, which encourages the feature descriptors for matching points to be similar and encourages the distance between the feature descriptors for non-matching keypoints to be large.
Feature Matching
-
Given keypoints produced by a pair of images, NN can learn to improve the matching of keypoints between images. SuperGlue gave the idea , it iteratively updated on self and cross features as the following figure:
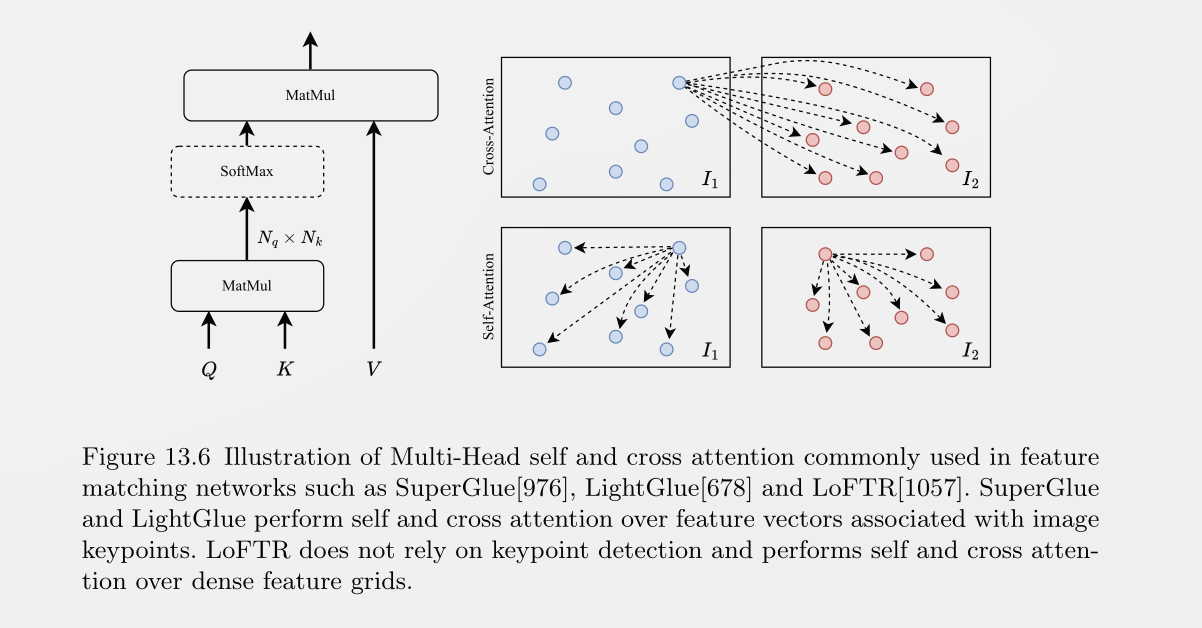
-
It also showed that it could improve accuracy on several other downstream tasks such as pose estimation. LightGlue as the successor, improved accuracy and speed of SuperGlue with some architecture and training improvements.
-
Limitation: They( glue brothers ) have the limitation because they operate on sparse points so dense matching is an issue, LoFTR tried to solve this by performing self and cross attention , and performed dense matching over coarse resolution feature grids, then refined the predictions at higher resolution.
-
These can help improve the robustness of SLAM systems in cases where traditional feature descriptors are stupid.
Optical Flow and RAFT
Watch this from the author of RAFT,RAFTv2, Droid and DPVO himself.
Optical Flow: It is the task of estimating per-pixel motion between a pair of frames. This per-pixel motion–or flow field–can be used as measurements in a factor graph-based visual SLAM system.
A lot of people have dirtied their hands on doing this , starting with (Dosovitskiy Alexey) as one of the founding authors in FlowNet, yes he's the same person who authored the image is worth 16x16 pixels. Coming to the point, it started with Google and Team making FlowNet 2016ish, then we have this predicting Flow using CNNs and Pyramid ( a spatial pyramid network SPyNet) then came FlowNet 2.0.
Let's see RAFT in more detail, as it's used in Droid .
Although current flow networks have improved on RAFT with multi-head attention and transformer blocks.
RAFT
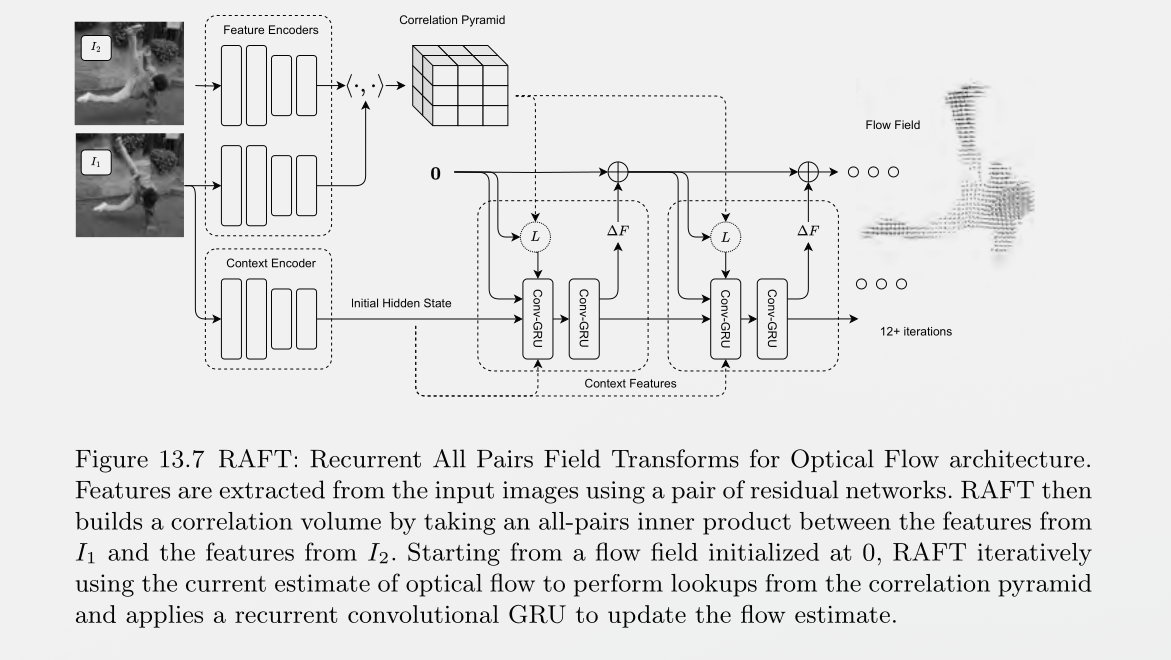
Features are first extracted from input images then those are used to build a 4D correlation volume.Starting with a flow field initialized at zero, the flow field is used to perform lookups from the correlation pyramid. The correlation features, alongside the current estimate of the flow field, are plugged into a Convolutional-GRU which produces an update to the flow field in addition to an updated hidden state.
Note: I don't really understand this in extreme details, will update here after going through the paper more. But the above paragraph is the overview.
Note: To be Added.
Optical Flow as Visual Measurements
- Optical Flow can be modeled as a function of depth and camera poses.
- Optical Flow Model
Estimating Pose and Depth from Optical Flow
- So now assuming you went through the Optical Flow model, we will try to find T and d from optical flow. Just reversing the Optical Flow problem.
SO WHAT IS A FACTOR GRAPH?
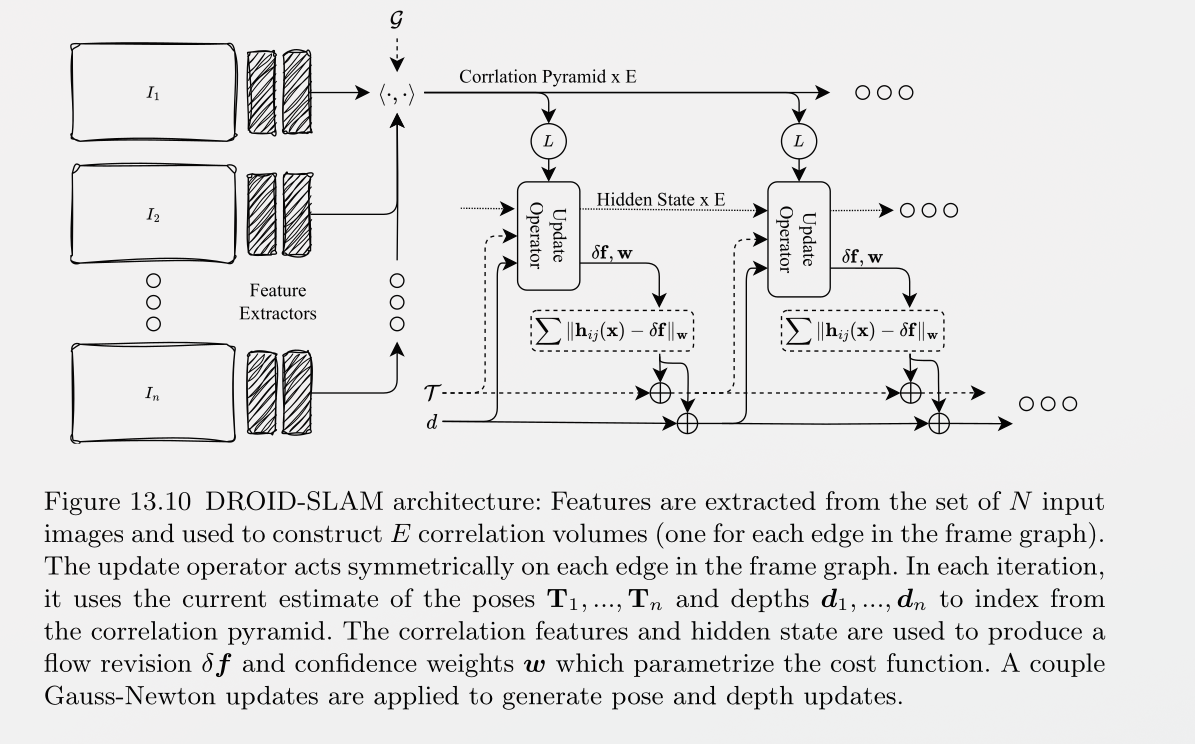
Differentiable Bndle Adjustment and DROID-SLAM
DROID-SLAM