Differential Amplifier using Transistors
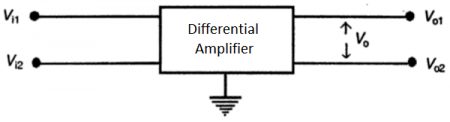
As the name indicates, Differential Amplifier is a dc-coupled amplifier that amplifies the difference between two input signals. It is the building block of analog integrated circuits and operational amplifiers (op-amp). One of the important features of the differential amplifier is that it tends to reject or nullify the part of input signals which is common to both inputs. This provides very good noise immunity in many applications. Let’s see the block diagram of a differential amplifier.
Differential Amplifier
Vi1 and Vi2 are input terminals, and Vo1 and Vo2 are output terminals with respect to ground. We can feed two input signals at the same time or one at a time. In the former case, it is called dual input; otherwise, it is single input. Similarly, there are two ways to take output as well. If the output is taken from one terminal with respect to ground, it is unbalanced output. If the output is taken between two output terminals, it is balanced output.
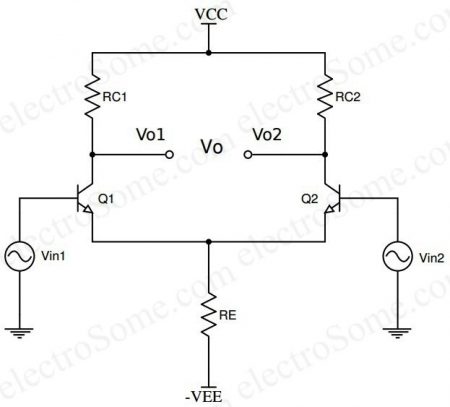
Differential Amplifier using BJT
The simplest form of differential amplifier can be constructed using Bipolar Junction Transistors (BJTs), as shown in the circuit diagram below. It is constructed using two matching transistors in common emitter configuration whose emitters are tied together.
Configurations
Based on the methods of providing input and taking output, differential amplifiers can have four different configurations:
- Single Input Unbalanced Output
- Single Input Balanced Output
- Dual Input Unbalanced Output
- Dual Input Balanced Output
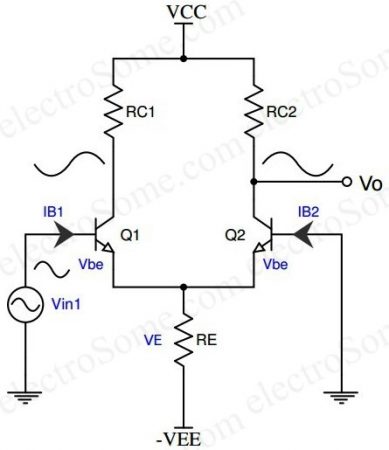
Single Input Unbalanced Output
In this configuration, only one input signal is given, and the output is taken from only one of the two collectors with respect to ground, as shown below.
When input signal
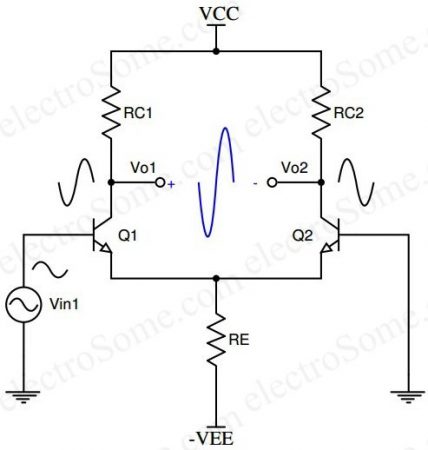
Single Input Balanced Output
In this case, only one input signal is given, but the output is taken from both collectors.
The output combines the effects of both transistors, providing a more amplified version with no unnecessary DC content.
Dual Input Unbalanced Output
Both inputs are given in this configuration, but the output is taken from only one collector.
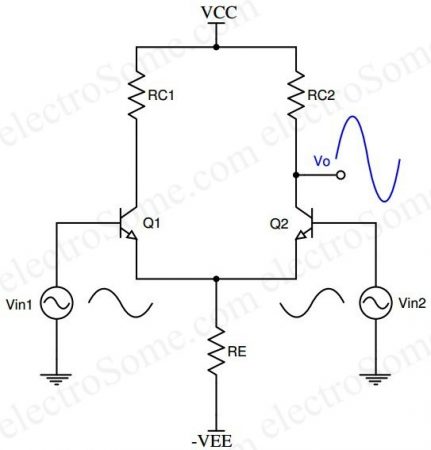
Dual Input Balanced Output
This configuration consists of two identical transistors
The output voltage is:
Where
DC Analysis
DC analysis determines the operating point values
[
Key equations for DC analysis:
1.
2.
AC Analysis
AC analysis determines the voltage gain
Key result for voltage gain:
Where