Schools of Thought

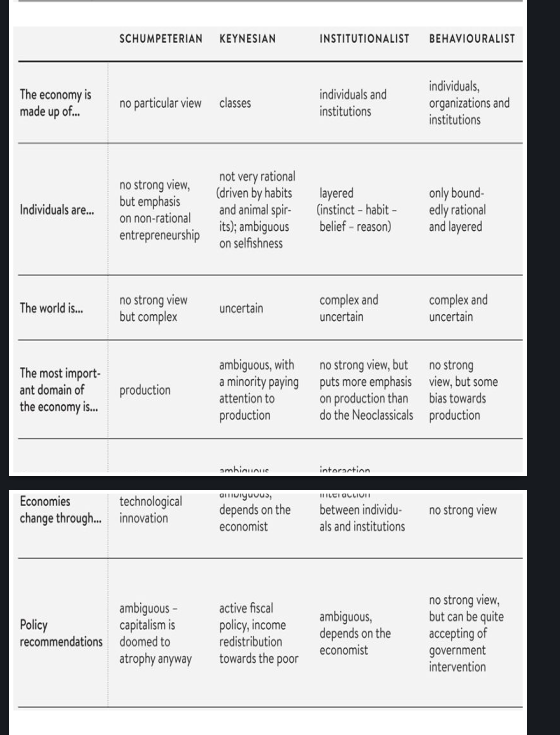
| Perspective | Classical | Neoclassical | Marxist | Keynesian | Institutionalist | Behaviouralist |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Economy is made up of… | Classes | Individuals | Classes | Classes | Individuals and institutions | Individuals, organizations, and institutions |
| Individuals are… | Selfish and rational (class-based) | Selfish and rational | Selfish and rational (except workers fighting for socialism) | Not very rational (driven by habits and animal spirits); ambiguous on selfishness | Layered (instinct → habit → belief → reason) | Only boundedly rational and layered |
| The world is… | Certain (“iron laws”) | Certain with calculable risk | Certain (“laws of motion”) | Uncertain | Complex and uncertain | Complex and uncertain |
| Most important domain of economy… | Production | Exchange and consumption | Production | Ambiguous, with a minority focusing on production | No strong view, but more emphasis on production than Neoclassicals | No strong view, but some bias toward production |
| Economies change through… | Capital accumulation (investment) | Individual choices | Class struggle, capital accumulation, technological progress | Ambiguous, depends on economist | Interaction between individuals and institutions | No strong view |
| Policy recommendations | Free market | Free market or interventionism (depends on failures) | Socialist revolution and central planning | Active fiscal policy, income redistribution toward the poor | Ambiguous, depends on economist | No strong view, but often accepting of government intervention |
Classical: The Market remains free, competition auto balances it.
Invisible Hand (Free Market) ( Adam Smith)
- Believes in the invisible hand that guides the market if the demand/supply decreases. (comes from Wealth of Nation by Adam Smith)
- Workers, Capitalists and landlords are the key class structure in this idea.
- If everyone acts on their selfish intent the market will be good for all because this invisible hand will guide it to manage itself, and government shouldn't interfere here.
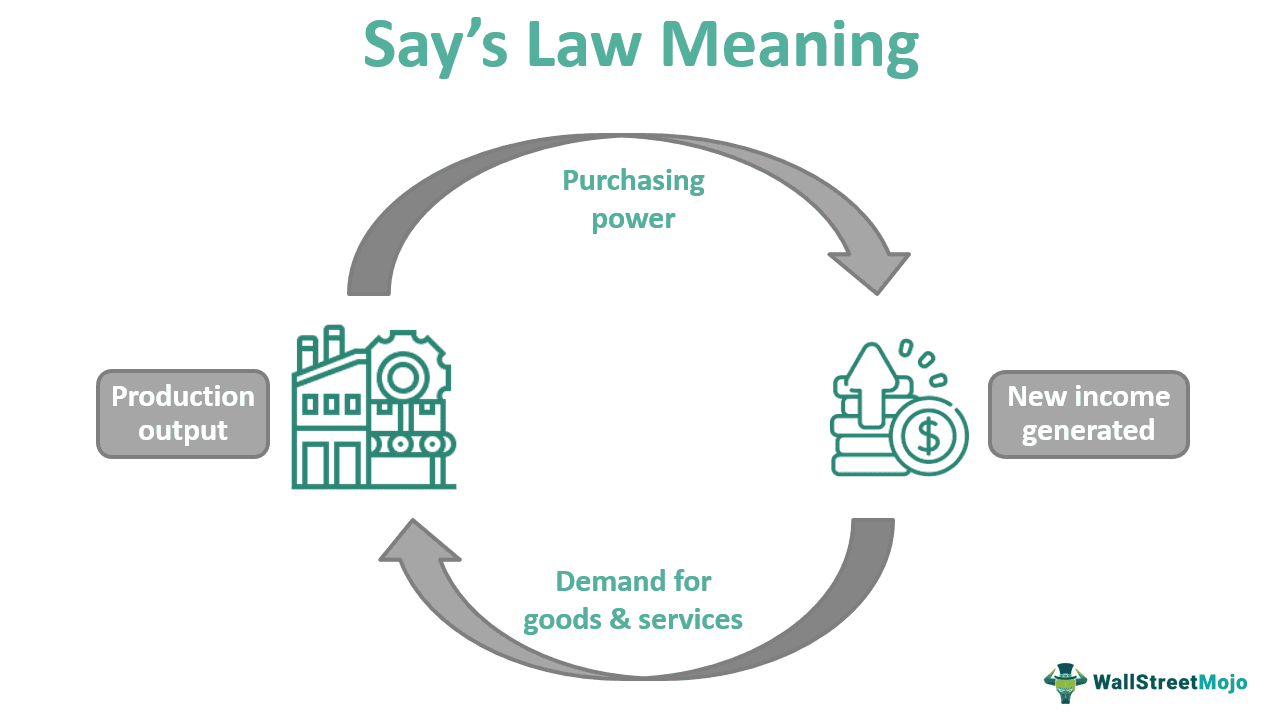
Say's Law
- Supply creates it's own demand.
Comparative Advantage ( Ricardo )
- Each state( nation ) should be more focused on what they are comparatively better at , this will be better for the market.
- For example, if Britain is making cotton, wine and ships and France is making Cotton and Wine, but France is better at making Wine compared to Britain, then Britain should focus more on making cotton(being good at what they specialize.) It strengths the free trade .
- Maximize output for all the nations that are involved in free trade.
Limitations:
- Say's Law is just wrong, doesn't account for macroeconomics issues like unemployment,recession( he just denies that recession will never happen if we continue to free trade )
Neo-Classical : Individuals are rational beings so give them independence, until and unless market is stable.
Labour Theory of Value
- It says that the value of a product(commodity) is determined by the amount of time/effort ( labor) has been put into it.
- ( Neo-Classical Doesn't Believe in that btw)
- Neo-Classical would say, just because something is really hard to make doesn't mean it's worth more.
- Marshall: demands matter short-run, supply matter long-run.
Analytics
- Uses analytics , calculus and mathematics in general to analyze the market.
- Assumes people are rational actors and make decision to maximize their satisfaction ( utility ) given their limited resources.
Marginalism
- an economic law that states that all else being equal , as consumption increases , satisfaction decreases from each additional unit.
General equilibrium theory
Marxian Economics: Capitalism is powerful but it will collapse, as private property ownership becomes a hindrance to further progress.
Mode of Production ( economic base)
- Production is basis of social order:
- Forces of Production include technologies,machinery, skills, factories etc.
- Relations of production include employments, division of labour etc.
- Superstructure(culture, politics, art) rests on this base and influences it. ( not related to forces of production directly kinda )
Historical Stages & Class Struggle
- Societies evolve through modes of production ( primitive communism, antiquarian, feudalism, capitalism, communism).
- Class conflict is the thing that drives this historical (social ) change.
Nature of Work
- Work can be creative as welll but it is dehumanizing under capitalism due to fine divisions of labour (alienation). and this just comes under theory of alienation
Production Focus & Theory of the Firm
- Focuses on production, unlike Neoclassical focus on exchange.
- Saw firms as 'islands of planning' in the market's 'anarchic sea'.
- Foresaw the rise of large joint-stock companies (corporations).
Keynesian : What is good for an individual isn't usually good for the whole economy.
Macroeconomics:
- Kinda invented this as he studied the whole of economy and how it is affected by the economic actors .
- Macroeconomics: branch of eco that deals with performance, structure , behavior and decision-making of an economy as a whole.
Recession and Ideas Around It:
- He argued against the idea of self-balancing markets, he said it's impossible and there's a flaw when we reach recession.
- He said we shouldn't thrift ( save ) during a recession, but rather spend, government should do their best to spend more money creating more jobs increasing the GDP.
- If everyone saves, people get laid off, they also save, prices go up, economy goes down.
- We need fiscal/monetary policies during recession.
- Eg: Government can make a bridge, so we get more workers, employment increases, they spend more so overall economy boosts.
The main policy prescription from Keynesian theory is the necessary role of governments in boosting demand through public investment
Institutional Economics: Individuals are product of society, even though they can change it's rules.
Ideas:
- Challenges classical and neo-classical for underplaying or bare right ignoring the social conditions of individuals in an economy.
- Individuals are shaped by society: the rise of the Institutionalist school.
- Human motivation is layered (instinct, habit, belief, reason). Rationality is context-dependent.
Institutions (Formal & Informal Rules)
-
Focuses on analyzing formal rules (laws, company policies) and informal rules (customs, social norms) that shape behaviour and the economy.
-
Institutions both constrain and shape individuals.
Transaction Costs
- Focuses on the costs of organizing economic activity: finding information bargaining , monitoring, making contracts.
- Institutions (rules, firms) actually rise to minimize these costs.
Behavioural Economics: We aren't that deep so we gotta constrain ourselves our own freedom through rules.
Kinda rejects the Neo-Classical theory by saying individuals aren't rational and gives examples.
Bounded Rationality (Herbert Simon)
- People try to be rational but their reasoning is limited to their understanding and comprehension of the world
- Information processing capacity is often the key limitation.
Role of Emotion, Loyalty, Fairness
- Emotion focuses attention.
- loyalty reduces monitoring costs
- perceived fairness builds loyalty.
Organizational Routines & Institutions as Rules
- Organizations and social institutions develop rules(routines kinda) to compensate for individual cognitive limits, simplify problems, and make their behaviour predictable. As in like enforcing rules as we aren't smart enough
Heuristics ( mental shortcuts ) & Satisficing
- People use mental shortcuts (heuristics, rules of thumb, pattern recognition) to ease decisions.
- People aim for 'good enough' outcomes (satisfice) but that doesn't lead to the absolute best (optimize).