Optimal Demodulation & Performance
this is first coz i forget lol
Signal Space and AWGN Model
- Core Idea: Represent
possible transmitted continuous-time signals as vectors in an -dimensional signal space ( ). - AWGN Channel Model (Vector Form): The received vector
when signal is sent is: is the noise vector. Its components are i.i.d. Gaussian . - The noise variance per real dimension is related to the physical noise PSD
by .
Optimal Decision Rules (Minimizing Probability of Error)
- MAP (Maximum A Posteriori) Rule: Optimal overall. Requires prior probabilities
. Choose hypothesis that maximizes the posterior probability . - Decision Metric (Equivalent): Choose
that maximizes: - Vector Form: Choose
that minimizes:
- Decision Metric (Equivalent): Choose
- ML (Maximum Likelihood) Rule: Optimal when priors
are equal. Chooses hypothesis that maximizes the likelihood . - Decision Metric (Equivalent): Choose
that maximizes: - Vector Form (Minimum Distance Rule): Choose
that minimizes:
- Decision Metric (Equivalent): Choose
- Implementation: Using a bank of correlators (computing
) or matched filters (output sampled at peak = ).
Performance Metrics: Geometry and SNR
Euclidean Distance
- The distance between signal points in the constellation is crucial for performance.
- Minimum Distance (
): The smallest distance between any two distinct constellation points. Often dominates performance at high SNR.
Energy per Bit (
- Relates average signal energy to the information transmitted.
- Average Energy per Symbol:
(assuming equal priors). - Energy per Bit:
represents the energy required per information bit.
Noise Power Spectral Density (
- Fundamental measure of noise level (power per Hz, one-sided). Directly related to noise variance per dimension:
.
Q-Function
- Tail probability of a standard Normal distribution
. Used to express error probabilities involving Gaussian noise.
Performance Formulas (ML, Equal Priors)
Pairwise Error Probability (PEP)
- The probability of deciding
when was sent, assuming only these two possibilities exist.
Binary Signaling Error Probability (
- Directly uses the pairwise error probability with
.
M-ary Symbol Error Rate (SER,
- Exact calculation is complex. Bounds and approximations are used.
- Union Bound: Upper bounds the probability of error by summing PEPs.
- Average SER:
- Average SER:
- Nearest Neighbor Approximation (High SNR): Assumes errors are dominated by mistaking a signal for one of its nearest neighbors at distance
. : Average number of nearest neighbors at distance .
Efficiency Metrics
Power Efficiency (
- Concept: How effectively does the constellation use energy to create distance between points? A measure of noise immunity for a given
. Often implicitly compares to BPSK. - Formal Definition (Binary Context): For binary signaling, we related
to : - For antipodal BPSK,
. For orthogonal/OOK, .
- For antipodal BPSK,
- M-ary Context: Instead of defining a single
, performance is typically analyzed via and . The quantity acts as a figure of merit for power efficiency when comparing constellations (higher is better). It tells us how much squared minimum distance we get per unit of energy-per-bit. - From the NN approx:
. - For high SNR, the argument of the Q-function dominates. Larger
leads to smaller for the same .
- From the NN approx:
Bandwidth Efficiency (
- Concept: How many bits are sent per second per Hertz of bandwidth?
- Formula (using Nyquist minimum bandwidth
for complex signals): - For real baseband (1D):
. - If excess bandwidth
is used: , so (complex).
- For real baseband (1D):
Linkages and Tradeoffs
- Pe vs. Geometry & SNR: The error probability
fundamentally depends on the ratio of minimum distance ( ) to noise standard deviation ( ). - Pe vs.
: We typically express performance as vs. . The relationship involves the constellation geometry via : - A constellation with a higher
(better power efficiency) will achieve a lower for the same .
- A constellation with a higher
- Power-Bandwidth Tradeoff:
- Increasing constellation size
generally increases bandwidth efficiency ( ). - Increasing constellation size
(for PAM, PSK, QAM) generally decreases power efficiency (reduces ) because points are packed closer for the same average energy . - Orthogonal signaling is an exception (power efficiency improves with M, bandwidth efficiency decreases).
- Increasing constellation size
Analog Modulation
Things to Remember
- Don't just blindly apply Carson, there could be cases where the signal isn't symmetric, remember the formula isn't 2(B+fmax) but 2(B+fmax+ - fmin-).
Chapter 1: Introduction
Basic Communication System
- Goal: Transfer information reliably and efficiently from a Source to a Destination across a Channel.
- Fundamental Blocks: Source
Transmitter Channel Receiver Destination. - Transmitter: Encodes source information into a signal suitable for the channel (modulation).
- Channel: The physical medium (wire, fiber, air, storage medium, etc.) that carries the signal. Introduces challenges.
- Receiver: Processes the received (corrupted) signal to estimate the original information (demodulation, decoding).
- Information Transfer: Can be across space (telephony, broadcasting, internet browsing) or time (data storage like CDs, DVDs, hard drives, cloud).
The Channel: Resource and Challenge
- The channel is the resource enabling communication but presents challenges.
Channel Challenge: Limited Spectrum/Bandwidth
- Physical media cannot support infinite frequencies. Transmission must occur within allocated/supported bands.
- Wired: Medium characteristics impose inherent frequency limits (e.g., high-frequency attenuation in copper pairs).
- Wireless: A scarce, regulated resource. Different frequency bands have different properties:
- Low frequencies: Require large antennas, offer low bandwidth.
- High frequencies: Suffer high attenuation, require line-of-sight (esp. > 5 GHz).
- Motivation: Leads to the need for bandwidth-efficient communication techniques and spectrum sharing strategies.
Channel Challenge: Noise and Interference
- Noise: Unavoidable random perturbations corrupting the signal.
- Thermal Noise: Fundamental, due to random motion of electrons.
- Other Sources: Man-made EMI, powerline interference, cosmic noise, shot noise.
- Model: Typically modelled as Additive White Gaussian Noise (AWGN). Additive (
), White (flat Power Spectral Density, PSD), Gaussian (amplitude distribution).
- Interference: Signals from other users/systems sharing the medium.
- Motivation: Need for techniques robust to noise and interference (e.g., signal design, error control coding, spread spectrum).
Channel Challenge: Distortion
- Attenuation: Signal weakening with distance/frequency. Varies across different frequencies in wired/wireless channels.
- Multipath (Wireless): Signal arrives via multiple paths due to reflections. Causes:
- Time-varying channel gain (fading).
- Delay spread: Symbols interfere with subsequent symbols (Inter-Symbol Interference - ISI).
- Linear Time-Invariant (LTI) Model: Often used for wired channels or short-duration wireless channels.
. - Linear Time-Variant (LTV) Model: Needed for wireless channels with mobility.
. - Motivation: Requires equalization techniques at the receiver to combat distortion and ISI.
Channel Challenge: Sharing and Limited Capacity
- Sharing: Wireless/wired resources often need to be shared among many users (e.g., cellular, WiFi, Ethernet). Leads to congestion, collisions, need for multiple access protocols.
- Limited Capacity (Shannon's Theorem): Defines the maximum theoretical rate (bits/sec) for reliable communication over a noisy channel.
- Fundamental trade-off between bandwidth (
), signal power ( or ), noise power ( ), and data rate ( ).
- Fundamental trade-off between bandwidth (
- Motivation: Benchmarks performance, drives search for efficient coding/modulation, highlights resource limitations.
Analog vs. Digital Communication
- Analog: Information (message signal) is a continuous-time, continuous-valued waveform (e.g., speech, audio). Transmitter directly maps message to transmitted analog signal.
- Examples: AM/FM radio, analog TV, vinyl records, 1st gen cellular (AMPS).
- Simple: Conceptually straightforward (Fig 1.1 / Slide 38).
- Susceptible to Noise: Noise accumulates through repeaters.
- Digital: Information (message signal) is represented by discrete values (often bits). Analog signals are first converted (sampled & quantized).
- Examples: Modern cellular (2G onwards), digital TV/radio, CDs/DVDs, data networks.
- Digital System Blocks (Fig 1.2 / Slide 41): Source Encoder (Compression)
Channel Encoder (Error Control) Modulator Channel Demodulator Channel Decoder Source Decoder. - Source Encoder: Converts source info to bits efficiently (removes redundancy). E.g., Huffman coding, ZIP, JPEG, MP3.
- Channel Encoder: Adds controlled redundancy tailored to the channel for error detection/correction. E.g., repetition code.
- Modulator: Maps bits/symbols to analog waveforms suitable for the channel (deals with bandwidth/power constraints).
- Demodulator/Decoder: Reverse processes at the receiver.
- Why Digital? (Sec 1.1.3 / Slide 53):
- Robustness: Regenerative repeaters clean noise/distortion perfectly (if errors are corrected).
- Optimality (Source-Channel Separation): Design source coding (compression) and channel coding (error control + modulation) independently for optimal performance (huge gains). Not possible in analog.
- Scalability & Flexibility: Networking (Internet relies on digital packets), integration of diverse services, easy storage, DSP implementation, cheaper hardware.
- Performance: Arbitrarily low error rates possible via channel coding (Shannon's theorem).
- Security: Encryption is readily applied to digital data.
- Role for Analog: Physical world and channels are analog. Digital systems need analog front-ends: DACs, ADCs, amplifiers, mixers, filters, antennas. RF/analog design remains crucial (Sec 1.1.4).
Chapter 2: Signals and Systems Fundamentals
Signal Representations (Sec 2.2)
- Continuous Time (CT):
- Discrete Time (DT):
(often from sampling ) - Indicator Function:
if , otherwise. Used for defining pulses, e.g., . (Slide 73) - Sinusoid: Basic periodic signal
. - Polar Form: Amplitude
, frequency , phase . - Rectangular Form:
. - Complex Representation:
. (Slide 75)
- Polar Form: Amplitude
- Complex Exponential:
where . Contains amplitude and phase. gives the real sinusoid. (Slide 76) - Delta Function
: Idealized impulse. Defined by sifting property . - Sinc Function:
. (Note: definition varies; this is common in comms).
Inner Product, Energy, Power (Sec 2.2)
- Inner Product (CT):
. (Slide 77) - Energy (CT):
. (Slide 78) - Power (CT, for signals not having finite energy): Time average of energy.
- DC Value:
. Zero for sinusoids with .
LTI Systems and Convolution (Sec 2.3)
- Linear Time-Invariant (LTI): Output is convolution of input
and impulse response . - Frequency Domain:
. (Slide 89) - Complex Exponentials are Eigenfunctions:
.
Fourier Analysis (Sec 2.4, 2.5)
- Fourier Series (Periodic Signals):
. (Slide 84) - Fourier Transform (Aperiodic/Finite Energy): (Slide 85)
- Properties: Linearity, Time/Freq Shift, Differentiation, Parseval, Convolution <=> Multiplication. (Slides 86-89)
- Key Pairs:
; ; . (Slide 91)
Spectral Density and Bandwidth (Sec 2.6)
- ESD (Finite Energy):
. Total Energy . (Slide 102) - PSD (Finite Power / WSS Processes):
. Total Power . - Bandwidth: Defines frequency occupancy.
- Strictly Bandlimited:
outside a band. (Slide 104, 105) - Fractional Power Containment: Smallest band containing
of energy/power. (Slide 107) - 3dB Bandwidth: Width where
is above half its peak value. (Slide 108) - For Real Signals: Only positive frequencies count (one-sided bandwidth). (Slide 105)
- For Complex Signals: Both positive and negative frequencies count. (Slide 106)
- Strictly Bandlimited:
Baseband and Passband (Sec 2.7)
- Baseband Signal: Spectrum concentrated around DC.
for . (Slide 110) - Examples: Source signals (speech, audio), baseband digital pulses. (Slide 111)
- Passband Signal: Spectrum concentrated around
, away from DC. for , with . (Slide 112) - Examples: Modulated signals for wireless transmission. (Slide 113, 114)
- Channels: Can also be baseband (e.g., twisted pair) or passband (e.g., wireless channel allocation). (Slide 116, 117)
Complex Baseband Representation (Sec 2.8)
- Motivation: Unify analysis of baseband and passband signals/systems. Most signal processing happens in complex baseband. (Slide 118)
- Representation: Real passband
Complex baseband . - Three Views (Slide 130, 131):
- I/Q Components (Rectangular):
.
. (Slide 123) - Envelope and Phase (Polar):
, .
. (Slide 128) - Complex Envelope:
. Links the two. (Slide 129)
- I/Q Components (Rectangular):
- Orthogonality:
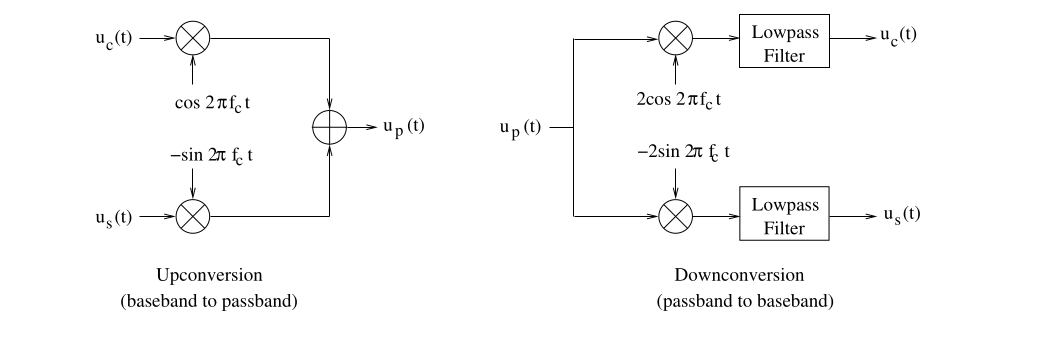
and carriers are orthogonal. Allows independent transmission on I and Q. (Slide 125) - Upconversion/Downconversion (Modulation/Demodulation): (Slide 126, 127)
- Multiply by
and carriers, then use LPFs.
- Multiply by
- Effect of Frequency/Phase Offset: If local oscillator has offset
and phase offset , i.e., , the received complex envelope is rotated: . This mixes I/Q components. (Slide 132) - Requires Coherent Detection: Receiver must synchronize its LO frequency and phase (
) or compensate for the offset. (Slide 133)
- Requires Coherent Detection: Receiver must synchronize its LO frequency and phase (
- Frequency Domain: (Slide 135, 136, 137)
- Reconstruction:
where is positive frequency part.
- Reconstruction:
- Filtering Equivalence: Passband filtering
is equivalent (up to scaling) to complex baseband filtering . Implemented using 4 real convolutions. (Slide 139, 141) - Energy/Power:
. (Slide 142) - Correlation:
. (Slide 143) - Modern Architecture: DSP operates on complex baseband samples. (Slide 144)
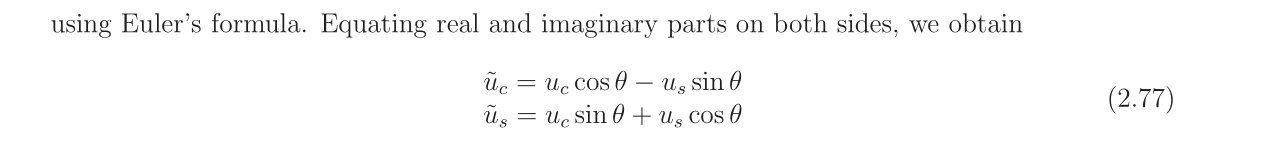
Chapter 3: Analog Communication Techniques
Motivation (Slide 148)
- Understand underlying physical signals even in digital era.
- Common language with circuit designers.
- Analog-centric techniques critical when pushing limits (low power, high speed).
- Concepts like PLL, Superhet remain relevant.
Terminology (Sec 3.1 / Slides 149-151)
- Message Signal:
, real-valued, baseband, often assumed zero mean ( ). Power . - Transmitted Signal:
, passband. Can be written via I/Q ( ) or Env/Phase ( ).
Amplitude Modulation (AM) (Sec 3.2)
DSB-SC (Double Sideband Suppressed Carrier) (Sec 3.2.1)
- Generation:
. Complex envelope . (Slide 156) - Spectrum:
. . (Slide 157, 159) - Demodulation: Requires coherent detector. Multiply by
, then LPF. Output . Needs phase sync. (Slide 160, 164)
Conventional AM (Sec 3.2.2)
- Generation:
. Large carrier added. (Slide 166) - Spectrum: DSB spectrum + impulses at
. (Slide 167) - Envelope Detection: If modulation index
, envelope . Recover message with simple diode+RC circuit. (Slide 168-171, 173, 175, 176, 180, 181) - Modulation Index:
. (Slide 173) - RC Time Constant:
. (Slide 177, 181) - Power Efficiency: Low due to carrier power.
. (Slide 192) - Modulators: Can use non-linear devices or switching modulators instead of ideal multipliers. (Slide 185-188)
SSB (Single Sideband) (Sec 3.2.3)
- Motivation:
. Most bandwidth efficient AM. (Slide 199) - Generation:
- Filtering: Ideal filter removes one sideband (hard). (Slide 200, 201)
- Phase Shift:
. Uses Hilbert Transform. (Slide 208-211, 216, 217)
- Complex Envelope:
. (Slide 217) - Demodulation: Coherent detection needed. Very sensitive to phase errors (crosstalk + attenuation). (Slide 221) Envelope detection possible if large carrier added. (Slide 222)
QAM (Quadrature Amplitude Modulation) (Sec 3.2.5)
- Generation:
. Two independent messages. (Slide 224) - Complex Envelope:
. - Demodulation: Coherent detection needed. Sensitive to phase errors (crosstalk). (Slide 226)
VSB (Vestigial Sideband) (Sec 3.2.4)
- Compromise between SSB (bandwidth) and DSB (filter simplicity). (Slide 228)
- Filter leaves a "vestige" of the unwanted sideband.
- Design criterion:
over message band ensures recovered as I component. (Slide 229)
Angle Modulation (Sec 3.3)
- Constant envelope
. Information in phase . (Slide 235, 237) - Phase Modulation (PM):
. - Frequency Modulation (FM): Instantaneous frequency
. . - Equivalence: FM is PM with integrated message; PM is FM with differentiated message. (Slide 238-240)
- Non-linearity: Angle modulation is a non-linear operation. (Slide 242)
- Preference: FM preferred for analog (smoother phase); PM often base for digital (PSK). (Slide 243, 244)
- Modulation Index (FM):
. (Slide 246) - Bandwidth:
- Narrowband FM (
): . Similar to AM. - Wideband FM (
): . Dominated by frequency deviation. - Carson's Rule: General estimate
. (Slide 260, 263)
- Narrowband FM (
- Spectrum (Sinusoidal Message): Involves Bessel functions
. Complex envelope spectrum . (Slide 264-268) - Modulation: Typically uses VCO (Voltage Controlled Oscillator). Direct or Indirect FM. (Slide 247)
- Demodulation:
- Limiter-Discriminator: Limiter removes amplitude variation, Discriminator converts freq variations to amplitude variations (e.g., differentiator + envelope detector, or slope detector). (Slide 250-252)
- PLL (Phase Locked Loop).
Receiver Architectures (Sec 3.4)
- Superheterodyne: Mix RF to fixed IF. Principle: Sloppy RF filter (image reject), sharp IF filter (channel select). Tradeoff between image rejection and adjacent channel rejection based on IF choice. (Slide 279, 284, 287, 289)
- Mixer: Non-linear device creating sum and difference frequencies. (Slide 285)
- Image Frequency:
. Unwanted signal that also mixes down to IF. Must be rejected by RF filter. - Direct Conversion: Mix directly to baseband (zero-IF). Avoids image issue, simpler integration. Challenges: DC offset, LO leakage, 1/f noise. (Slide 291, 292)
- mmWave: May revive Superhet due to ADC limitations, or use hybrid architectures. (Slide 293)
Phase Locked Loop (PLL) (Sec 3.5)
- Concept: Feedback loop: Phase Detector compares input phase
and VCO output phase ; error drives VCO via Loop Filter. (Slide 296, 297) - Phase Detectors: Mixer-based (output
) or logic-based (XOR, phase-frequency detector). (Slide 298-302) - Applications: (Slide 125)
- FM Demodulation: VCO input tracks message
if loop tracks . (Slide 304) - Frequency Synthesis: Use frequency divider in loop to synthesize high frequency LO from stable low frequency reference. (Slide 305)
- FM Demodulation: VCO input tracks message
- Mathematical Model: Non-linear due to phase detector. (Slide 308)
- Linearized Model: Assumes small phase error
. Allows LTI analysis using Laplace transforms. (Slide 309-312) - Loop Order & Tracking:
- 1st Order (G(s)=1): Tracks phase steps with zero steady-state error. Cannot track frequency steps (has steady-state phase error
). (Slide 313, 314, 315) - 2nd Order (G(s)=1+a/s): Tracks frequency steps with zero steady-state phase error. (Slide 316, 317)
- 1st Order (G(s)=1): Tracks phase steps with zero steady-state error. Cannot track frequency steps (has steady-state phase error
- Non-linear Behavior: Locking range depends on loop gain K vs frequency offset
. Phase plane analysis useful. (Slide 321-324)
Chapter 4: Digital Modulation
Signal Constellations (Sec 4.1)
- Mapping bits to complex symbols
. Plotted on I/Q plane. (Slide 331, 338) - Linear Baseband Model:
. (Slide 328) - Linear Passband Model:
. (Slide 329) - Examples:
- BPSK (2-PAM):
. Baseband or Passband (phase shifts 0, ). (Slide 330, 332) - 4-PAM:
. Baseband. (Slide 333) - QPSK (4-PSK / 4-QAM):
. Passband (phase shifts ). (Slide 334, 335, 336, 337) - M-PSK: Points on a circle.
- M-QAM: Points on a grid.
- BPSK (2-PAM):
Bandwidth Occupancy (Sec 4.2)
- Requires statistical description (symbols
are random). - Power Spectral Density (PSD): Characterizes power distribution vs frequency for finite power signals / WSS processes. (Slide 342)
- Periodogram Estimation: Estimate PSD from finite observation window
: . PSD is limit as . (Slide 343) - PSD of Linearly Modulated Signal (Thm 4.2.1): If symbols are zero mean and uncorrelated with average energy
: - Power
. (Slide 344)
- Power
- Bandwidth Definitions based on PSD: (Slide 347)
- 3dB Bandwidth.
- Fractional Power Containment Bandwidth.
- Time/Frequency Normalization: Analyze system with
, then scale bandwidth by . (Slide 348, 349) - Example: Rectangular Pulse:
. Wide tails, poor bandwidth containment. (Slide 350) - Example: Sine Pulse:
has much better decay. (Slide 353)
Design for Bandlimited Channels (Sec 4.3)
- Motivation: Match signal spectrum to channel bandwidth, avoid ISI. (Slide 371, 372)
- Nyquist Sampling Theorem (Thm 4.3.1): Signal bandlimited to
is determined by samples at rate . . (Slide 368) - Implies
complex dimensions / second in bandwidth .
- Implies
- Nyquist Criterion for Zero ISI (Thm 4.3.2): (Slide 376)
- Time:
(pulse zero crossings). - Frequency:
. (Aliased spectrum is flat).
- Time:
- Sinc Pulse:
. Minimum BW . Problem: Slow decay causes large ISI with timing errors. (Slide 369, 375, 381, 382) - Need for Excess Bandwidth: Pulses decaying faster than
(like or ) require bandwidth but mitigate ISI issues. (Slide 385) - Trapezoidal Pulse (Freq): Convolution of two rects.
. Decays as . (Slide 386-389) - Raised Cosine (RC) Pulse (Freq): Smoother rolloff than trapezoid.
. Decays as . (Slide 395, 396) - Excess Bandwidth (
): Factor by which BW exceeds minimum . . - Nyquist Rate Property: A pulse Nyquist at rate
is also Nyquist at rates for integer . (Slide 390)
Bandwidth Efficiency (Sec 4.3.3)
. For complex baseband, complex dim, or 2 real dims. - For Nyquist pulse with excess
, using dimensions/symbol seems intuitive but the standard definition ignores : - Rate
(bits/sec). Min BW . Actual .
Power-Bandwidth Tradeoffs (Sec 4.3.4)
- Increase
Increase . - Requires more power for same reliability.
- Power Efficiency (Scale Invariant):
. Depends only on constellation shape. - Performance depends on
and .
Orthogonal Modulation (Sec 4.4)
- Concept: Uses M mutually orthogonal signals
over a symbol duration . - Motivation: Improve power efficiency compared to bandwidth-efficient constellations like QAM, especially for large M. Bandwidth efficiency is sacrificed. (Slide 402)
- Orthogonality Definitions: (Slide 408)
- Coherent: Requires
for . - Non-coherent: Requires
for (stricter).
- Coherent: Requires
- Examples:
- FSK (Frequency Shift Keying): Uses M sinusoidal tones separated by
. (Slide 403) - Coherent requires
. (Slide 404) - Non-coherent requires
. (Slide 407) - Bandwidth
.
- Coherent requires
- Walsh-Hadamard Codes: Orthogonal sequences modulated onto a chip pulse (see Sec 4.3.6, 7.4).
- FSK (Frequency Shift Keying): Uses M sinusoidal tones separated by
Coherent vs Non-coherent FSK
- Coherent Demodulation: Uses a bank of correlators matched to each tone (requires phase synchronization). (Slide 405)
- Issue with Coherent: Highly sensitive to phase errors. A
phase offset makes the desired correlator output zero. (Slide 406) - Non-coherent Demodulation: Uses energy detectors or magnitude correlations
. Does not require phase sync but needs larger frequency separation ( ). (Slide 407)
Bandwidth and Power Efficiency (Orthogonal)
- Bandwidth: Coherent requires
; Non-coherent requires . - Bandwidth Efficiency:
. Coherent uses complex dimensions ( ); Non-coherent uses complex dimensions ( ). Both as . (Slide 408) - Power Efficiency (Asymptotic): M-ary orthogonal signaling achieves the best possible power efficiency (
dB) as . (See Chapter 6 discussion).
Biorthogonal Modulation (Sec 4.4)
- Construction: Start with an
-ary orthogonal set and add their antipodal versions . Total signals. - Applicability: Only for coherent systems (non-coherent detection cannot distinguish
from ). - Bandwidth Efficiency:
. Twice that of M-ary orthogonal for the same M, using the same number of dimensions. (Slide 409)
Chapter 5: Probability and Random Processes (Selected Topics)
Noise Modeling (Sec 5.8 / Slides 412-421)
- Noise: Any undesired signal corrupting the desired signal. (Slide 413)
- Sources:
- Natural: Thermal noise (fundamental), atmospheric noise, cosmic noise.
- Man-made: Interference, power-line hum, electronic device noise (shot noise, flicker noise).
- Thermal Noise (Johnson-Nyquist): Due to random thermal agitation of charge carriers (electrons) in resistive components. (Slide 414)
- Mean-square voltage across resistor R in bandwidth B:
. - Noise power delivered to matched load:
. - Noise Power Spectral Density (PSD):
(one-sided). PSD is flat ("white") for practical frequencies ( THz at room temp). (Slide 415)
- Mean-square voltage across resistor R in bandwidth B:
- White Noise Model: Noise PSD is flat over the bandwidth of interest.
- Passband:
for . One-sided . Power . (Slide 416) - Baseband:
for . One-sided . Power . (Slide 417) - Unified WGN Model: Assume PSD is flat
for all frequencies. Autocorrelation . Simplifies analysis as receiver filtering imposes band limitation. (Slide 418, 420)
- Passband:
- Gaussian Noise Model: Noise amplitudes follow Gaussian distribution. Justified by Central Limit Theorem (noise results from many microscopic random events). (Slide 419)
- AWGN Model: Combines Additive, White, and Gaussian assumptions. Standard model for many communication channels.
- Noise Figure (F): Ratio of actual noise PSD (
) to ideal thermal noise ( ). . . (Sec 5.8) - Noise Power Calculation (dBm):
. (Slide 421)
Linear Operations on Random Processes (Sec 5.9)
Filtering (Sec 5.9.1 / Slides 422-428)
- Input: Random process
. Filter: LTI system . Output: . (Slide 423) - Gaussianity Preservation: If
is Gaussian, is Gaussian. - WSS Preservation: If
is WSS, is WSS. (Slide 425) - Output PSD:
. (Slide 424) - Output Autocorrelation:
where . (Slide 425) - Output Power:
. - Example: WGN through Filter: Input
. Output . Output power . (Slide 427, 428)
Correlation (Sec 5.9.2 / Slides 429-434)
- Operation:
. is random process, is deterministic template. (Slide 429) - Mean of Z:
. - Variance of Z (if
, is WGN): (Derived for real case, Slide 431) - Signal component:
(deterministic). - Noise component:
. . .
- Signal component:
- Signal-to-Noise Ratio (SNR) for Correlator:
- Max SNR =
.
- Max SNR =
- Filter as Correlator: Correlation
is equivalent to filtering with and sampling the output at . (Slide 433) - Matched Filter Implementation: The optimal correlator
can be implemented by filtering with and sampling at (or if signal is ). (Slide 434)
Chapter 6: Optimal Demodulation
Hypothesis Testing Framework Review (Sec 6.1 / Slides 447-456)
- Goal: Decide which of M hypotheses
(signal was sent) is true, given observation . Minimize . - Key Components: Hypotheses, Observation, Conditional densities
, Prior probabilities . - MAP Rule (Optimal): Choose
maximizing . Equivalent to maximizing . (Slide 450) - ML Rule: Choose
maximizing (Likelihood). Equivalent to MAP for equal priors ( ). (Slide 452) - Binary Case & Likelihood Ratio Test (LRT): Decide
if . Threshold for ML. (Slide 453, 455, 456)
Signal Space Concepts (Sec 6.2 / Slides 457-476)
- Mapping CT to DT: Represent M signals
as n-D vectors using an orthonormal basis spanning the signal space S. (Slide 458, 464) - Gram-Schmidt: Procedure to construct an orthonormal basis from a set of signals (useful conceptually). (Slide 465-468)
- Inner Products Preserved:
. (Slide 469) - WGN in Signal Space: (Slide 470)
- Project noise
onto basis: . (Slide 471) - Theorem 6.2.1:
are i.i.d. . Noise vector . (Slide 473) - Geometric View: Projection of WGN in any direction is
; projections onto orthogonal directions are independent. (Slide 474)
- Project noise
- Irrelevance of Orthogonal Noise: Noise component
orthogonal to signal space is independent of and contains no signal information. Can be discarded. (Slide 476)
Optimal Reception in AWGN (Sec 6.2.4 / Slides 477-487)
- Model: Receive vector
, where . (Slide 475) - Conditional Density:
. - ML Rule: Minimize distance
. (Slide 477) - MAP Rule: Minimize
. - Mapping back to CT: (Slide 482, 484)
- ML: Choose
maximizing . - MAP: Choose
maximizing .
- ML: Choose
- Implementation: Correlator bank or Matched Filter bank. (Slide 485, 486)
- Complex Baseband Implementation: Perform equivalent operations using complex baseband signals and filters. (Slide 487)
Performance Analysis (Sec 6.3 / Slides 488-520)
- Focus: ML rule (equal priors).
- Geometry of Errors: Error occurs if noise
causes received vector to fall into another decision region . For pairwise decision between , error occurs if noise component perpendicular to boundary exceeds distance . (Slide 490, 491) - Binary Signaling:
where is power efficiency. (Slide 491, 495, 496) - Comparison: Antipodal (
) is 3dB better than Orthogonal/OOK ( ). (Slide 497, 498)
- Comparison: Antipodal (
- M-ary Signaling Scale Invariance: Performance depends only on
and constellation shape (defined by normalized inner products ). (Slide 501) - Exact Analysis: Difficult for
due to correlated noise components across boundaries (requires multi-dimensional integration). (Slide 504) - QPSK: Exact
. (Slide 502) - Approximations/Bounds:
- Union Bound:
. Overestimates, especially at low SNR. (Slide 505, 506, 508) - Intelligent Union Bound: Sum only over neighbors defining the decision region. Tighter. (Slide 509, 510)
- Nearest Neighbor Approximation:
. Good at high SNR. (Slide 513)
- Union Bound:
- Example: 16QAM: NNA
. Comparison with QPSK shows ~4dB power penalty for doubling bandwidth efficiency. (Slide 515-517) - M-ary Orthogonal: (Slide 518, 519)
- Exact SER requires complex integral involving
. - UB
. - Asymptotic performance:
required as . Power efficient, bandwidth inefficient.
- Exact SER requires complex integral involving
- Bit Error Rate (BER): Estimated from SER using bit mapping. Gray coding minimizes BER for a given SER. For Gray code,
. (Sec 6.4)
Link Budget Analysis (Sec 6.5)
- Connects required
(from BER target) to physical link parameters. - Receiver Sensitivity: Minimum required
based on , , and Noise Figure . - Friis Formula: Relates
to , antenna gains ( ), range ( ), wavelength ( ). - Link Budget Equation: Combines sensitivity, gains, path loss, and link margin to determine required
or achievable range .